The various benefits of grits are related to their high nutritional content. The southern United States has a large market for grits. Although they taste like tofu, they usually absorb flavors from the paired food. The thick and creamy texture is achieved by cooking the ground dried corn in broth or water.
This breakfast food is packed with essential nutrients, making it a favorite (1). However, experts are still studying grits to learn more about their health benefits. Here, we have compiled a few ways grits may enrich your diet. This article discusses the importance of grits, their benefits, nutritional profile, and possible side effects. Take a look.
Stylecraze TriviaThe area stretching from Texas to Virginia is called the “Grits Belt”, which accounts to over 75% of the total grit sales in the U.S..
In This Article
What Are The Health Benefits Of Grits?
Grits are good sources of fiber, making them a good option to include in a diabetes diet. Their zeaxanthin content may help promote eye health. The lack of gluten in grits means they could be consumed by those who are sensitive to gluten.
1. May Aid Diabetes Treatment
Shutterstock
Studies show that pure, high-quality corn grits have a lower glycemic response compared to milled rice or other varieties. This could be partly related to a better dietage-related macular degenerationary fiber composition of corn grits. These grits may be more beneficial for those with diabetes (2).
However, grits could be higher in carbs. Also, grits made from non-fermented corn flour may have a low glycemic index of 90 (3). Hence, it is important to pick the right variety. Try using stone-ground grits and try cooking them with water or broth as they are healthier options.
Related: Easy Ways To Lower Blood Sugar Naturally And Safely
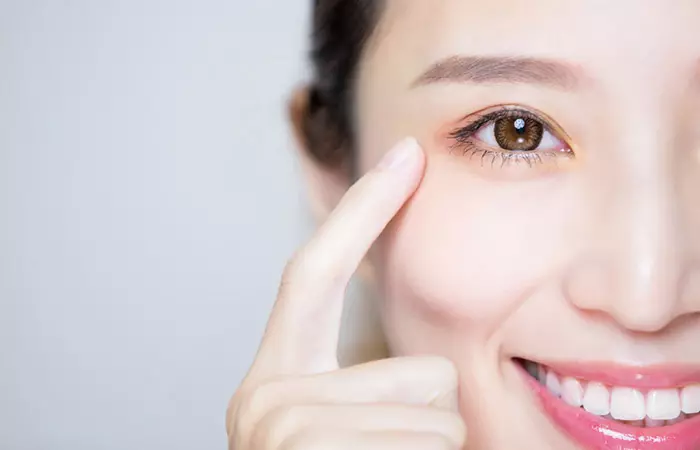
2. May Help Boost Vision Health

Shutterstock
Corn is one of the few food sources rich in dietary zeaxanthin, as per a report. Zeaxanthin is a major carotenoid that is thought to protect against the development of age-related macular degeneration (4).
Related: 15 Best Foods To Improve Eyesight Naturally
3. May Help In Treating Anemia
Shutterstock
Grits are a good source of iron (1). The most common form of anemia is one that is caused by iron deficiency (5). Although there is no direct research correlating grits and anemia, consuming grits may help in mitigating iron deficiency.
Iron deficiency can be prevented through food diversification, supplementation, and fortification (6). Corn grits can also be fortified with iron for better nutrition. In a rat study, the addition of 2 grams of ferric citrate to corn grits increased their content by an additional 3.1 milligrams of iron per gram of diet (7).
Related: 27 Foods That Boost Your Hemoglobin Levels
4. Are Gluten-Free

Shutterstock
One major advantage of grits is that they are gluten-free. Grits belong to the same family as wheat, barley, rye, and spelt. But if you are gluten intolerant or have celiac disease, you can include corn grits in your diet (8).
These are a few major benefits of corn grits. As more research unfolds, we will have more information on how this food can help better your health.
We saw a couple of important nutrients in grits. But there is a whole range of other nutrients that you may want to look at.
What Is The Nutritional Profile Of Grits?
| Name | Amount | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Water | 10.92 | g |
| Energy | 370 | kcal |
| Energy | 1549 | kJ |
| Protein | 7.65 | g |
| Total lipid (fat) | 1.75 | g |
| Ash | 0.6 | g |
| Carbohydrate, by difference | 79.09 | g |
| Fiber, total dietary | 4.6 | g |
| Sugars, total including NLEA | 0.57 | g |
| Sucrose | 0.57 | g |
| Starch | 68.23 | g |
| Calcium, Ca | 4 | mg |
| Iron, Fe | 3.05 | mg |
| Magnesium, Mg | 36 | mg |
| Phosphorus, P | 111 | mg |
| Potassium, K | 141 | mg |
| Sodium, Na | 1 | mg |
| Zinc, Zn | 0.72 | mg |
| Copper, Cu | 0.03 | mg |
| Manganese, Mn | 0.145 | mg |
| Selenium, Se | 17 | µg |
| Thiamin | 1.271 | mg |
| Riboflavin | 0.339 | mg |
| Niacin | 4.465 | mg |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.253 | mg |
| Vitamin B-6 | 0.233 | mg |
| Folate, total | 171 | µg |
| Folic acid | 132 | µg |
| Folate, food | 39 | µg |
| Folate, DFE | 263 | µg |
| Choline, total | 14.4 | mg |
| Betaine | 1.1 | mg |
| Carotene, beta | 1 | µg |
| Cryptoxanthin, beta | 1 | µg |
| Vitamin A, IU | 3 | IU |
| Lutein + zeaxanthin | 5 | µg |
| Vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol) | 0.21 | mg |
| Tocopherol, beta | 0.01 | mg |
| Tocopherol, gamma | 0.7 | mg |
| Tocopherol, delta | 0.04 | mg |
| Tocotrienol, alpha | 0.35 | mg |
| Tocotrienol, gamma | 0.97 | mg |
| Fatty acids, total saturated | 0.34 | g |
| Fatty acids, total monounsaturated | 0.315 | g |
| Fatty acids, total polyunsaturated | 0.875 | g |
| Tryptophan | 0.057 | g |
| Threonine | 0.277 | g |
| Isoleucine | 0.288 | g |
| Leucine | 1.154 | g |
| Lysine | 0.156 | g |
| Methionine | 0.182 | g |
| Cystine | 0.172 | g |
| Phenylalanine | 0.444 | g |
| Tyrosine | 0.175 | g |
| Valine | 0.383 | g |
| Arginine | 0.282 | g |
| Histidine | 0.234 | g |
| Alanine | 0.67 | g |
| Aspartic acid | 0.508 | g |
| Glutamic acid | 1.716 | g |
| Glycine | 0.26 | g |
| Proline | 0.883 | g |
| Serine | 0.375 | g |
Source: USDA, Cereals, corn grits, white, regular and quick, enriched, dry
Looking at this nutritional profile, it is no wonder that grits would make for a healthy breakfast or dinner. But how do you make them?
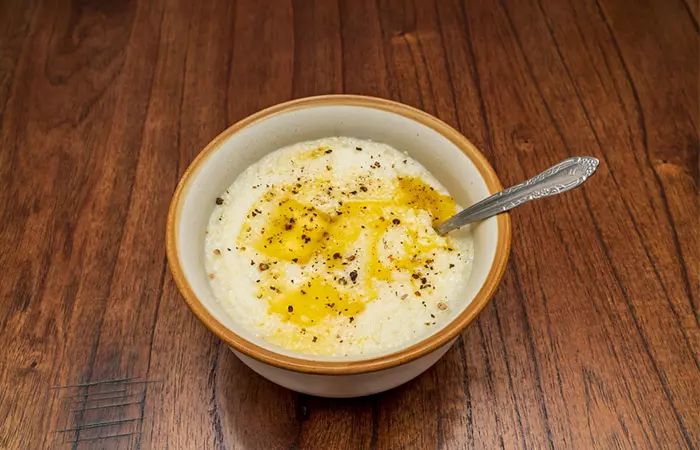
How To Prepare Grits At Home

Shutterstock
Preparing grits at home is simple.
What You Need
- 2 cups of water
- 1 teaspoon of salt
- 1 ¼ cups of milk
- ½ cup of butter
- 1 cup of quick-cooking grits
Directions
- In a small pot, bring the water, salt, and milk to a boil. Stir them to a boiling mixture, continuously, until they are well mixed.
- As the mixture comes to a boil, cover it with a lid and lower the temperature. Cook for about 30 minutes, stirring occasionally.
- Stir in half of the butter. Once the grits achieve a smooth consistency, you know they are done. You can serve with the remaining butter.
You can have grits as they are or try out different variations. You may mix a mashed banana into your grits and top it all with chopped walnuts. Or you may add a handful of blueberries and chopped almonds to your grits.
You can also purchase grits, either at your nearest supermarket or online.
SubscribeDid You Know?Grits are the official state-prepared food of Georgia, the state meal of Oklahoma, and the state food of South Carolina.
Though grits are healthy and preparing them is simple, there is something else about them you need to keep in mind.
Do Grits Have Any Side Effects?
Grits do not have any serious side effects. But they have certain disadvantages.
They are made by a process that removes the outer skin (called pericarp) and the embryo (the germ), leaving behind the endosperm, which is the starchy component (9).
The outer skin and the embryo are loaded with nutrients. The outer skin is also a good source of fiber.
Also, since grits are served along with ingredients like milk, butter, and syrups, which are high in calories, excess intake can lead to obesity in the long run.
Using more vegetables, fruits, and extra virgin olive oil, and less cheese or butter can be a healthier way of eating grits.
Grits are fiber-rich foods made from dried, ground corn in various liquids. They have a rich nutritional profile that helps treat many ailments. The intake of gluten-free delicious food sources like grits benefits your health in several ways. For example, they may aid in diabetes treatment, and their zeaxanthin content may help improve vision health and protect against age-related macular degeneration. Grits may also treat anemia, and they are an excellent food option for people with celiac disease. However, excess consumption of grits may lead to obesity in the long run due to their high calorific value. Hence, practice moderation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How are grits different from polenta?
While grits belong to South American cuisine, polenta belongs to Italy. Grits are made of white corn, and polenta is made from yellow corn. Both are made from ground corn, though. Also, both are often used interchangeably and are similarly nutritious.
Are grits better with milk or water?
Grits absorb both milk and water the same. You can have them along with a half-milk-half-water combination. That way, you can cut down the calories and enjoy the nutritional goodness of milk too.
Should you rinse grits?
It does not make a lot of difference, even if you do. If you are rinsing, you can gently clean them 4 to 7 times.
Are grits bad for a low-carb diet?
Grits may not be a great option for a low-carb diet as they are comparatively high in carbs. A cup of grits (156 grams) contains about 123 grams of carbs (1).
Are grits better than oatmeal?
Both are nutritious and offer unique nutritional profiles. Oatmeal is comparatively richer in antioxidants, but instant oatmeal can come with sugar that adds unnecessary calories. Grits, however, are not made with added sugar (in most cases).
You can have each, every alternate day. Be wary of the sugar in the oatmeal. As grits are not as high in antioxidants as oatmeal, you can have them with fresh veggies.
Can grits help with weight loss?
There is no research on this. Also, grits are comparatively higher in calories and are usually taken with ingredients that could also be calorie-dense. Hence, we do not recommend you add grits to your weight loss diet.
Sources
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Check out our editorial policy for further details.
- Cereals, corn grits, white, regular and quick, enriched, dry, US Department of Agriculture.
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171654/nutrients - Glycaemic Response to Quality Protein Maize Grits, Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2938446/ - Glycemic responses to maize flour stiff porridges prepared using local recipes in Malawi, Food Science and Nutrition, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4779488/ - Xanthophyll (lutein, zeaxanthin) content in fruits, vegetables and corn and egg products, Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, ScienceDirect.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0889157508001336?via%3Dihub - Iron-Deficiency Anemia, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/iron-deficiency-anemia - Review on iron and its importance for human health, Journal of Research in Medical Sciences, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3999603/ - THE INFLUENCE OF DIET ON IRON ABSORPTION, Journal of Experimental Medicine.
http://jem.rupress.org/content/jem/90/2/137.full.pdf - Gluten-Free Diet, Celiac Disease, Center at Columbia University Medical Center.
https://celiacdiseasecenter.columbia.edu/treatment/diet/ - Effects of Different Processing Methods on the Micronutrient and Phytochemical Contents of Maize: From A to Z, Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, Wiley Online Library.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/1541-4337.12216
Was this article helpful?
Related
The following two tabs change content below.
- Reviewer
- Author

Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Ravi Teja Tadimalla is an editor and a published author. He has been in the digital media field for over… more
Madhu Sharma
(RD)Madhu Sharma is a member of the National Executive Committee of IDA. She has been associated for almost three decades… more


 23 Amazing Benefits Of Mulberries (Shahtoot) For Skin, Hair, And Health
23 Amazing Benefits Of Mulberries (Shahtoot) For Skin, Hair, And Health 22 Best Benefits Of Oatmeal For Skin, Hair, And Health
22 Best Benefits Of Oatmeal For Skin, Hair, And Health 21 Amazing Benefits Of Litchis (Lychees) For Skin, Hair, And Health
21 Amazing Benefits Of Litchis (Lychees) For Skin, Hair, And Health 10 Nutritional Benefits Of Carrot Juice For Skin, Vision, And Health
10 Nutritional Benefits Of Carrot Juice For Skin, Vision, And Health Honey For Oily Skin – 12 Best Ways To Use It Effectively
Honey For Oily Skin – 12 Best Ways To Use It Effectively Flax Seeds Benefits & DIY Face Masks For Beautiful Skin
Flax Seeds Benefits & DIY Face Masks For Beautiful Skin Parsley: 10 Potential Benefits And Uses, Nutrition, How To Make Tea
Parsley: 10 Potential Benefits And Uses, Nutrition, How To Make Tea 33 Wonderful Benefits Of Banana For Skin, Hair, And Health
33 Wonderful Benefits Of Banana For Skin, Hair, And Health Tea Tree Oil For Warts: Benefits, How To Use, And More
Tea Tree Oil For Warts: Benefits, How To Use, And More